Leetcode 304. Range Sum Query 2D - Immutable
Explanation for Leetcode 304 - Range Sum Query 2D - Immutable, and its solution in Python.
Problem
Leetcode 304 - Range Sum Query 2D - Immutable
Example:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
Input
["NumMatrix", "sumRegion", "sumRegion", "sumRegion"]
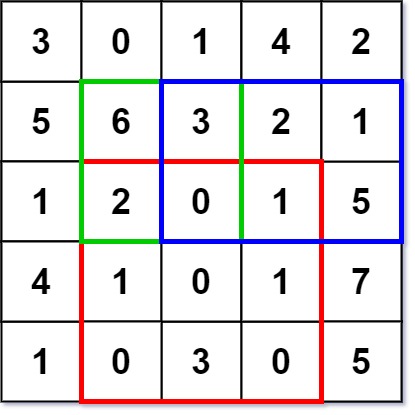
[[[[3, 0, 1, 4, 2], [5, 6, 3, 2, 1], [1, 2, 0, 1, 5], [4, 1, 0, 1, 7], [1, 0, 3, 0, 5]]], [2, 1, 4, 3], [1, 1, 2, 2], [1, 2, 2, 4]]
Output
[null, 8, 11, 12]
Explanation
NumMatrix numMatrix = new NumMatrix([[3, 0, 1, 4, 2], [5, 6, 3, 2, 1], [1, 2, 0, 1, 5], [4, 1, 0, 1, 7], [1, 0, 3, 0, 5]]);
numMatrix.sumRegion(2, 1, 4, 3); // return 8 (i.e sum of the red rectangle)
numMatrix.sumRegion(1, 1, 2, 2); // return 11 (i.e sum of the green rectangle)
numMatrix.sumRegion(1, 2, 2, 4); // return 12 (i.e sum of the blue rectangle)
Approach
We can solve this problem using the sum matrix when we initialize the matrix. Meaning that we create a sum matrix where all elements are the total sum of (0, 0) to (x, y) in (x,y) position. Once this is done, we can simply calculate the sum area of (r1,c1) to (r2, c2) by using this formula: (r2, c2) - (r1-1, c2) - (r2, c1-1) + (r1-1, c1-1)
Though this might be unclear right now after looking at the visualiztion of the approach it may be more clear
Visualization of the Approach:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
We want to get the sumRegion of (2, 1) to (4, 3) or from the image blue square
matrix: [3, 0, 1, 4, 2]
[5, 6, 3, 2, 1]
[1, 2, 0, 1, 5]
[4, 1, 0, 1, 7]
[1, 0, 3, 0, 5]
sumMatrix: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 ]
[0, 3, 3, 4, 8, 10]
[0, 8, 14, 18, 24, 27]
[0, 9, 17, 21, 28, 36]
[0, 13, 22, 26, 34, 49]
[0, 14, 23, 30, 38, 58]
We added extra row and column full of 0 for edge case
sumMatrix here indicates the sum of (0, 0) to (x, y). Meaning that at the whole sum at (4, 4) would be 58
in other words the whole square adds up to 58
As of the formula for getting the sum of (r1, c1) to (r2, c2) as said before is:
(r2, c2) - (r1-1, c2) - (r2, c1-1) + (r1-1, c1-1)
Meaning that the sumRegion of (2,1) to (4, 3) is equal to
(4, 3) - (1, 3) - (4, 0) + (1, 0) = 36 - 10 - 17 + 3 = 12
Here is the Python code for the solution:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
class NumMatrix:
def __init__(self, matrix: List[List[int]]):
ROWS, COLS = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
self.sumMat = [([0] * (COLS+1)) for _ in range(ROWS+1)]
for r in range(ROWS):
prefix = 0
for c in range(COLS):
prefix += self.sumMat[r][c]
above = self.sumMat[r][c+1]
self.sumMat[r+1][c+1] = prefix + above
def sumRegion(self, row1: int, col1: int, row2: int, col2: int) -> int:
row1, col1, row2, col2 = row1+1, col1+1, row2+1, col2+1
bottomRight = self.sumMat[row2][col2]
topRight = self.sumMat[row1-1][col2]
bottomLeft = self.sumMat[row2][col1-1]
topLeft = self.sumMat[row1-1][col1-1]
return bottomRight - topRight - bottomLeft + topLeft
Time Complexity and Space Complexity
Time Complexity: $O(1)$ since we’re just accessing the sumMat to get the sum
Space Complexity: $O(mn)$ since we’re storing the $mn$ matrix where $m$ is number of rows and $n$ is number of columns