How to handle Data, and Images(15) Number Recognition
Number Recognition using KNN Algorithm
Lesson Notes in .ipynb file
How to handle Data, and Images(15) - Number Recognition
Topics
Setting up
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
import cv2
import numpy as np
# the image includes handwritten numbers from 0-9. Consisting of 500 each
img = cv2.imread('digit.png')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# split the image 50 columns and 100 rows and put them into split
cells = [np.hsplit(row, 100) for row in np.vsplit(gray, 50)]
x = np.array(cells)
print(x.shape)
# reshape the (20x20) image into (1 x 400)
train = x[:, :].reshape(-1, 400).astype(np.float32)
print(train.shape)
# put each image from 0-9 into an array in correct index
k = np.arange(10)
train_labels = np.repeat(k, 500)[:, np.newaxis]
print(train_labels.shape)
np.savez('trained.npz', train=train, train_labels=train_labels)
Output:
1
2
3
(50, 100, 20, 20)
(5000, 400)
(5000, 1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# show the first index from 0
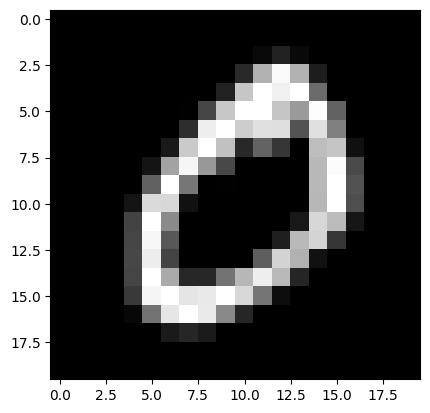
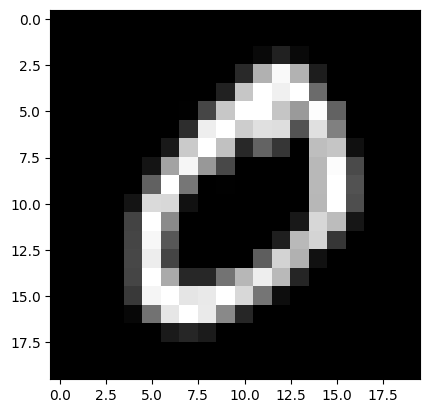
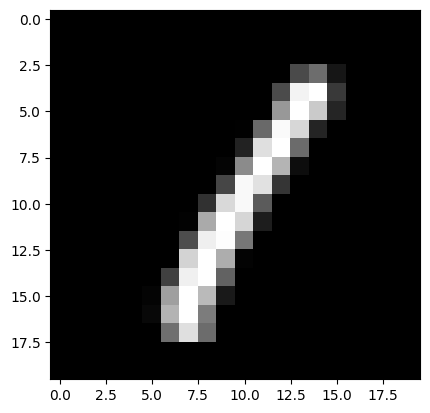
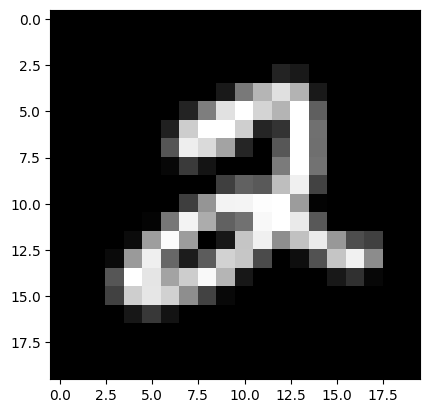
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(x[0, 0], cv2.COLOR_GRAY2RGB))
plt.show()
# you can save each image seperately
cv2.imwrite('test_0.png', x[0,0])
cv2.imwrite('test_1.png', x[5,0])
cv2.imwrite('test_2.png', x[10,0])
cv2.imwrite('test_3.png', x[15,0])
cv2.imwrite('test_4.png', x[20,0])
cv2.imwrite('test_5.png', x[25,0])
cv2.imwrite('test_6.png', x[30,0])
cv2.imwrite('test_7.png', x[35,0])
cv2.imwrite('test_8.png', x[40,0])
cv2.imwrite('test_9.png', x[45,0])
KNN number recognition
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
import cv2
import numpy as np
import glob
FILE_NAME = 'trained.npz'
# loading the training data and its labels
def load_train_data(file_name):
with np.load(file_name) as data:
train = data['train']
train_labels = data['train_labels']
return train, train_labels
# scaling the handwritten image to (20 x 20)
def resize20(image):
img = cv2.imread(image)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray_resize = cv2.resize(gray, (20,20))
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(gray_resize, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2RGB))
plt.show()
# returns the (1 x 400) size of image
return gray_resize.reshape(-1, 400).astype(np.float32)
def check(test, train, train_labels):
knn = cv2.ml.KNearest_create()
knn.train(train, cv2.ml.ROW_SAMPLE, train_labels)
# find the nearest 5 numbers and label itself
ret, result, neightbours, dist = knn.findNearest(test, k=5)
return result
train, train_labels = load_train_data(FILE_NAME)
for file_name in glob.glob('./test_*.png'):
# put the image down first
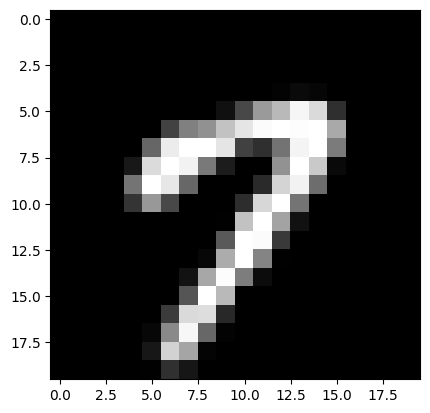
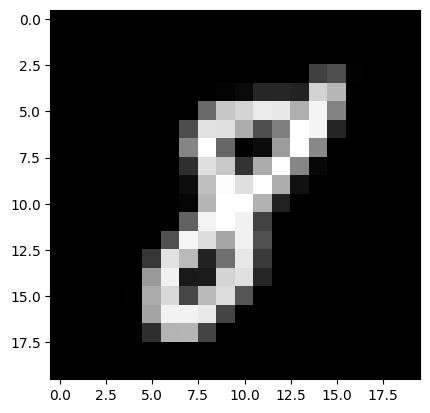
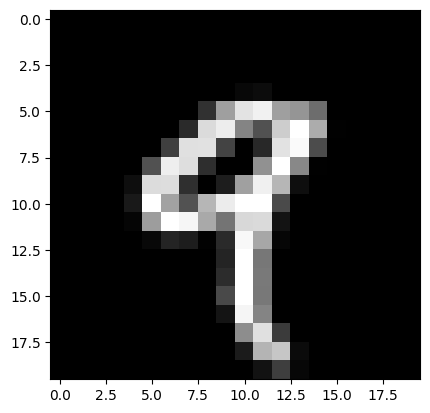
test = resize20(file_name)
result = check(test, train, train_labels)
# print the result
print(result)
Output:
Summary
Using KNN algorithm we were able to successfully determine the handwriting of the numbers
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.