How to handle Data, and Images(11) OpenCV Contours
How to get contours, and draw contours of image
Lesson Notes in .ipynb file
How to handle Data, and Images(11) - OpenCV Contours
Topics
OpenCV Contours
Input image must be Gray Scaled beforehand
cv2.findContours(image, mode, method): finding Contours from image returns (contours, hierarchy)
- mode: Contour retrieval mode
- RETER_EXTERNAL: it returns only extreme outer flags.
- RETER_LIST: It simply retrieves all the contours, but doesn’t create any parent-child relationship.
- RETER_TREE: It retrieves all the contours and creates a full family hierarchy list.
- method: Contour approximation method
- CHAIN_APPROX_NONE: stores absolutely all the contour points. That is, any 2 subsequent points $(x1,y1)$ and $(x2,y2)$ of the contour will be either horizontal, vertical or diagonal neighbors, that is, $max(abs(x1-x2),abs(y2-y1))==1$.
- CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE: compresses horizontal, vertical, and diagonal segments and leaves only their end points. For example, an up-right rectangular contour is encoded with 4 points.
cv2.drawContours(image, contour_index, color, thickness): Draws contours outlines or filled contours.
- contour_index: Parameter indicating a contour to draw. (all contours: -1)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# image1 is for contours_external, image2 is for contours_tree
image1 = cv2.imread('chanel.jpg')
image2 = cv2.imread('chanel.jpg')
# gray scale the image
image_gray = cv2.cvtColor(image1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# thresholding
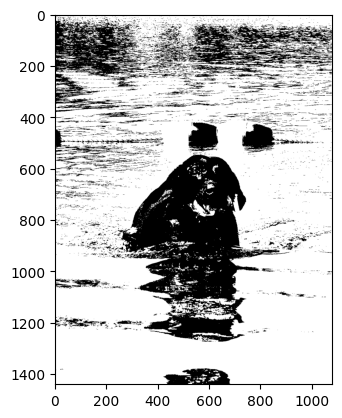
ret, thresh1 = cv2.threshold(image_gray, 127, 255, 0)
ret, thresh2 = cv2.threshold(image_gray, 127, 255, 0)
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(thresh1, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2RGB))
plt.show()
# have to return index 0, because cv2.findContours returns (contours, hierarchy)
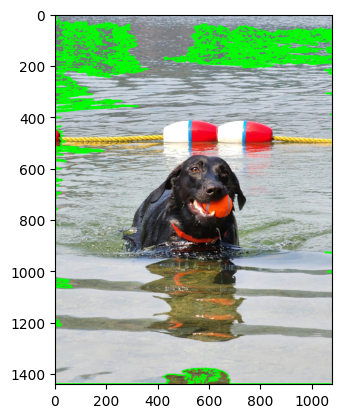
contours_external = cv2.findContours(thresh1, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[0]
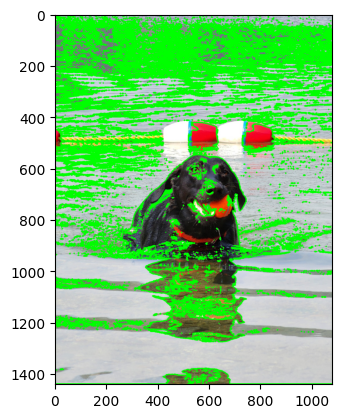
contours_tree = cv2.findContours(thresh2, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[0]
# show all contours of the image (we can select by adjusting the value '-1' to 0 to n)
external_image = cv2.drawContours(image1, contours_external, -1, (0, 255, 0), 4)
tree_image = cv2.drawContours(image2, contours_tree, -1, (0, 255, 0), 4)
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(external_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.show()
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(tree_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
plt.show()
Output:
Summary
- cv2.findContours(): finding Contours from image returns (contours, hierarchy)
- mode: Contour retrieval mode
- RETER_EXTERNAL: it returns only extreme outer flags.
- RETER_LIST: It simply retrieves all the contours, but doesn’t create any parent-child relationship.
- RETER_TREE: It retrieves all the contours and creates a full family hierarchy list.
- method: Contour approximation method
- CHAIN_APPROX_NONE: stores absolutely all the contour points. That is, any 2 subsequent points $(x1,y1)$ and $(x2,y2)$ of the contour will be either horizontal, vertical or diagonal neighbors, that is, $max(abs(x1-x2),abs(y2-y1))==1$.
- CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE: compresses horizontal, vertical, and diagonal segments and leaves only their end points. For example, an up-right rectangular contour is encoded with 4 points.
- mode: Contour retrieval mode
- cv2.drawContours(): Draws contours outlines or filled contours.
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.